The first step in querying your Microsoft SQL Server database is to connect FactBranch to your SQL Server instance. You do this by creating a SQL Server Data Source in FactBranch.
Once you've entered your credentials in the authentication, they are stored on FactBranch's servers, encrypted-at-rest and the password will never be shown again anywhere in your FactBranch account.
You can, however, use the authentication in your nodes. This allows you to save the credentials once and then re-use it in several nodes. You can even let another team member create nodes and use the data source without them seeing the credentials.
In this article you'll learn:
We recommend creating a dedicated user for FactBranch with only the permissions it needs to run your queries. Typically this means giving read-only access on the tables you will query.
This is a basic example of how to create an appropriate user in your SQL Server database. Use this as a starting point depending on your own requirements.
Create a SQL Server login and database user for FactBranch. Replace all values
surrounded by <...> with your own values.
-- Create a login at the server level
CREATE LOGIN factbranch WITH PASSWORD = '<PASSWORD>';
-- Switch to your database
USE <your_database>;
-- Create a user in the database
CREATE USER factbranch FOR LOGIN factbranch;
Grant the user read-only access to the databases and tables you want to query:
-- Grant read access to the entire database
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER factbranch;
-- Or grant read access to specific tables
GRANT SELECT ON <your_table> TO factbranch;
-- Or grant read access to specific schemas
GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA::<your_schema> TO factbranch;
If you're using Azure SQL Database, you can create the user using the same SQL commands above. Make sure your Azure SQL firewall rules allow connections from FactBranch's static IP address.
Note: For Azure SQL Database, you'll connect directly to the database (not to
the master database) and the server name will look like:
your-server.database.windows.net
To create a SQL Server authentication in FactBranch, click on Add data source in your Data Sources dashboard, then select Microsoft SQL Server. You'll be forwarded to the credentials form.
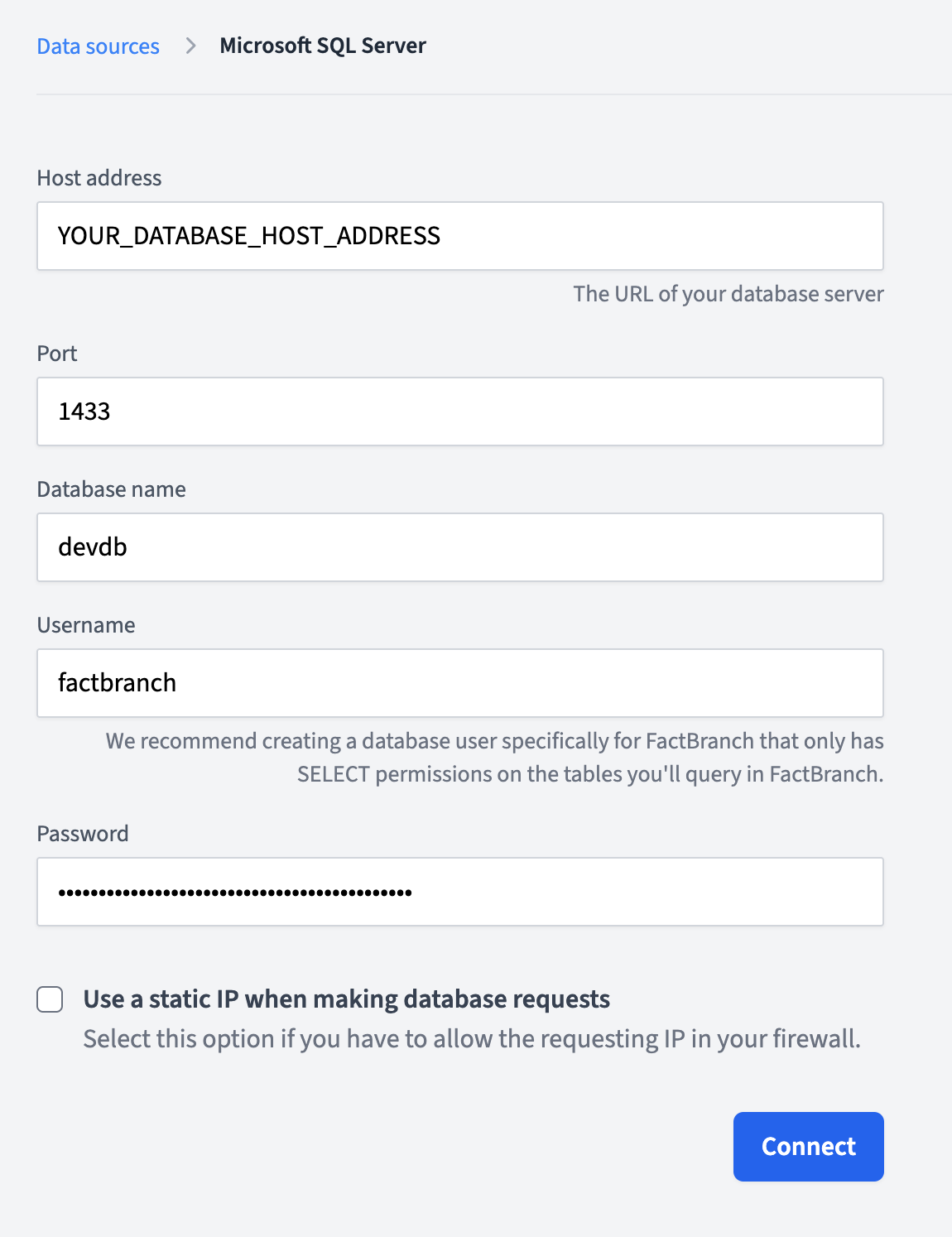
your-server.database.windows.net. For on-premises servers,
this might be an IP address or server name.factbranch.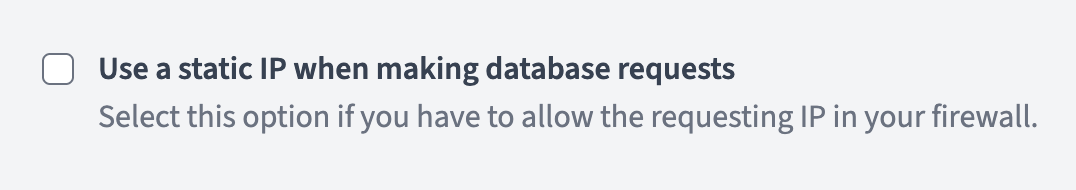
Once you've filled out everything, click Connect. FactBranch will test the credentials you've entered by attempting to connect to your database. If it was successful, you'll be forwarded to the list of data sources and you'll see your newly created SQL Server authentication in the list.
You can now use this authentication in a SQL Server node to run SQL queries in your SQL Server database.
To rename the data source, either click on Rename next to the title, or double-click on the title itself. Then enter the new name and click on Save or hit Enter on your keyboard. To revert to the old name, hit the Escape key.
First create a Microsoft SQL Server node in one of your Flows. Edit the node by clicking Edit next to the node in the Flow Editor. Select the Authentication tab on the left side of the screen. Then click on Select an authentication... - or on change... if that node already has an authentication associated. Select the authentication you'd like to use and from now on this node will use for all its requests the credentials you've stored in the authentication.
If you get a "connection refused" error, check that: - Your SQL Server instance is running and accessible - The host address and port are correct - Your firewall allows connections from FactBranch's static IP address - SQL Server is configured to accept TCP/IP connections - The SQL Server Browser service is running (if using named instances)
If you get an "access denied" error, verify that: - The username and password are correct - The login exists at the server level - The user exists in the target database - The user has been granted appropriate SELECT permissions
FactBranch connects using SSL by default for security. SQL Server supports encrypted connections. If you encounter SSL issues, check your SQL Server SSL/TLS configuration.
For Azure SQL Database:
- Make sure you're connecting to the correct database name (not master)
- Verify that your Azure SQL firewall rules include FactBranch's static IP
- Check that the server name includes .database.windows.net
- Ensure you're using SQL authentication (not Windows authentication)
If you're using a named SQL Server instance, you may need to specify the instance
name in the host field like: server-name\instance-name or use a specific port
number that the named instance is configured to use.